Vocab Blog from Lessons and Units
This is the vocab blog for all lessons in CSP. The definitions are above and the example is in the code cell right below the definition.
x = bin(2)
y = bin(4)
z = bin(8)
print(x,y,z)
Bytes: 8 bits.
Ex: 10110100
int(0b10110100)
Hexadecimal: a series of 6 digits representing color. It is base 16. It goes from 0-9 and then a-f.
Ex: RGB, #000000, #000001, etc.
print("#000000 = The color black")
Nibbles: 4 bits.
Ex: 1011
int(0b1011)
uInt = 10
if uInt >=0:
print(uInt,": ","This is an unsigned integer")
else:
print(uInt,": ", "This is not an unsigned integer")
Signed Integer: An integer that has a + or - sign and can be positive, negative, or zero.
sInt = 1
print(sInt,": ", "This is a signed integer.")
Floating point: The act of extending the binary number to accomodate small fractions or large integers.
x = int(0b10110)
y = int(0b11011)
concat = str(x)+"."+str(y)
print(concat)
print(100>99.9)
ASCII: An 8-bit code that uses eight bits to represent a letter or a punctuation mark.
x = int(0b01000001)
print("Decimal: ",x)
print("Binary: ", "01000001")
print("ACSII: ", "A")
y = int(0b01100001)
print("Decimal: ",y)
print("Binary: ", "01100001")
print("ACSII: ", "a")
Unicode: An international encoding standard where each letter, digit, or symbol is assigned with a unique numeric value.
print("U+0048: ", "h")
print("U+0065: ", "e")
print("U+006C: ","l")
print("U+006C: ", "l")
print("U+006F: ", "o")
print("prints 'hello'")
RGB: A color model where the primary colors of red, green, and blue are mixed together in different ways. It is in hexadecimal form.
print("#000000 = black")
print("#0000ff = blue")
print("#ffffff = white")
print("Let abcdefg represent the data in an image")
print("Compression: abcd")
print("Decompression: abcde(no longer its original form)")
Lossless: Restores the file's data to its original form during decompression.
print("Let abcdefg represent the data in an image")
print("Compression: abcd")
print("Decompression: abcdefg")
variable = 1
print(variable)
Data types: Data that can be stored in variables which represent different types and have different ways that they are used. In python, there are numeric, string, sequence, binary, mapping, boolean, and set data types.
x = 1
y = "hi"
z = [1,2,3,4,5]
q = 10>1
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
print(type(q))
Assignment operators: Things that assign values in relation to another value.
number = 1
number +=1
print(number)
list = ["hi","hello","how are you doing"]
print(list)
2D Lists: A list inside a list.
list2D = [
[1,2,3],
[1,2,3],
[1,2,3]
]
for i in list2D:
print(i)
Dictionaries: Stores data in key:value pairs.
dictionary = {
"number1" : 10,
"number2" : 20
}
print(dictionary)
Class: A blueprint for creating something.
class word:
print("hi")
print("hello")
Algorithm: Set of instructions to do a task.
def printStuff():
print("print")
print("more printing")
print("and more printing")
printStuff()
Sequence: A series of tasks in the order of specification
x = 10
y = 26
z = x+y
y = z+3
print(x,y,z)
Selection: Uses true/false to determine which code is executed.
x = 5>10
if x == True:
print("True")
elif x == False:
print("False")
Iteration: Repeats a code if condition is true.
list = [1,2,3,4]
for i in list:
print(i)
Expression: A combination of values and functions which creates a new value.
x = 1
y = 2
z = 3
sum = x+y+z
print(sum)
Comparison operators: operators used to compare two values.
x = 1
y = 1
if x ==y:
print("x=y")
Booleans Expressions and Selection: Selecting subsets of data based on their actual values rather than by their row/column.
list = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
for i in list:
if i == 2:#Selecting values using boolean
print(i)
Booleans Expressions and Iteration: Looping through a list and filtering out data using booleans.
x = [-2,-1,0,1,2]
for i in x:
if i>=0:#Boolean expression
print(i)
Truth Tables: Tables that display the results of logical operators AND, OR, XOR, and NOT using binary 1 and 0.
- Example from APCSP Fastpages:
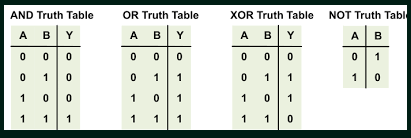
print("Example: OR")
print("1|0 = ", 1|0)
print("~(1|0) = ", ~(1|0)%2)
Characters: Letters and punctuation that are created using a specific binary value(ACSII) or a specific unicode value.
print("Z: ", 101101)
String: A data type involving a sequence of characters.
print("String")
Length: The number of characters in a string, or values in a list.
x = [1,2,3,4,5,2,4,5,2,4]
print(len("hello"))
print(len(x))
Concatenation: Combining multiple strings without leaving spaces in between.
x = "Hi, I'm"
y = "Alan"
z = x+y
print(z)
Upper string: Converts a string into all uppercases.
x = "hello how are you doing"
print(x.upper())
Lower string: Converts a string into all lowercases.
x = "I'M DOING WELL"
print(x.lower())
Traversing string: Displays only a part of the original string.
x = "Hello"
print(x[1:5])
Python If statement: Executes a segment of code if a certain condition is met.
x = 0
if x==0:
x +=1
print(x)
Python Elif statement: Executes a segment of code if a certain condition is met and after the If statements are false.
x = 1
if x==0:
print(x)
elif x ==1:
x+=1
print(x)
Python Else statement: Executes a segment of code if all the previous conditions of If and Elif statements are not met.
x = 0
if x == 1:
x+=2
else:
x+=1
print(x)
Nested selection statements: An if statement inside of an if statement.
x = 0
if x == 0:
x+=2
if x ==4:
print("hi")
elif x==2:
print("hello")
Python For loops with range: Iterates through a sequence of numbers.
for x in range(4):
print(x)
Python For loops with list: Iterates over a list.
x = [1,2,3,4,5]
for i in x:
print(i)
Python While loops with range: Iterating over the range given until it terminates by failing to meet the condition.
x= 0
while x<len(range(3)):
print("hi")
x +=1
Python While loops with list: Iterating over a list until it terminates by failing to meet the condition.
x = [1,2,3,4,5]
i = 0
while i<len(x):
print(x[i])
i +=1
Combining loops with conditionals to break: Exiting a loop using an if statement inside the loop.
x = [1,2,3,4,5,56,6,3,23]
for i in x:
print(i)
if i ==5:
break# exits loop
Combining loops with conditionals to continue: Stopping the current iteration of the loop and resuming right after.
x = [1,2,3,4,5,56,6,3,23]
for i in x:
if i ==5:
continue# Doesn't print 5
print(i)
Procedural Abstraction: The process of combining lines of code into multiple functions, making things easier and much more efficient when referring to them multiple times.
def printHi():
print("hi")
print("how")
print("are")
print("you")
print("doing")
def printBye():
print("bye")
print("see")
print("you")
print("later")
printHi()
printBye()
printHi()
printBye()
Python Def procedures: Creating functions that can execute code.
def functionExample():
print("This is an example")
functionExample()
Parameters: The variables listed inside the parentheses when defining a function.
def variable(n):
n +=1
print(n)
variable(2)
Return values: A value that a function returns to the caller.
def numberTest(n):
if n < 0:
return "negative"
else:
return "positive"
print(numberTest(-1))